
Hi, I’m higashi.
This time, I introduce how to calculate the intersection coordinate of designated two lines as shown below.
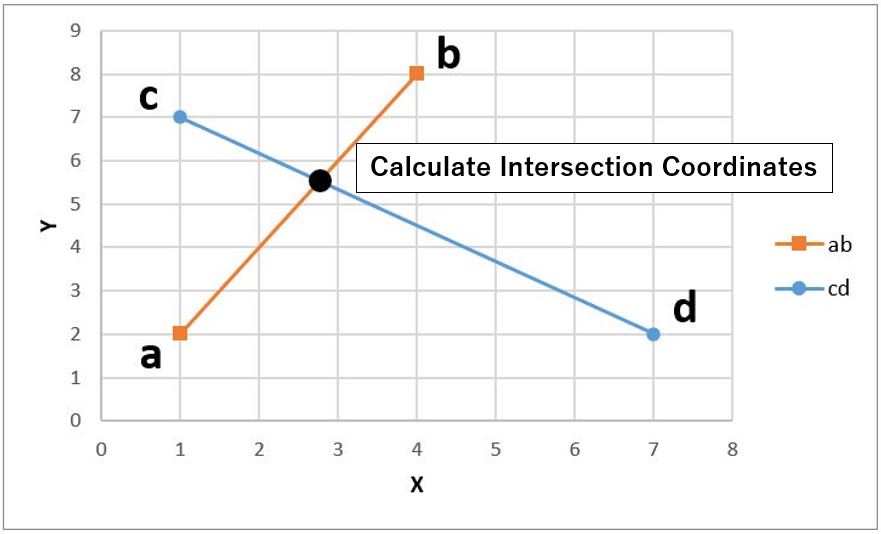
Just you have to do is designating the start and end points coordinate of two lines.
So, let’s get started!!
Illustration of How to Calculate the Intersection Coordinate
I illustrate how to calculate the intersection coordinate.
It is very simple method.
At first, set two arbitrary point on each line respectively.
And calculate the distance of two points as shown below.
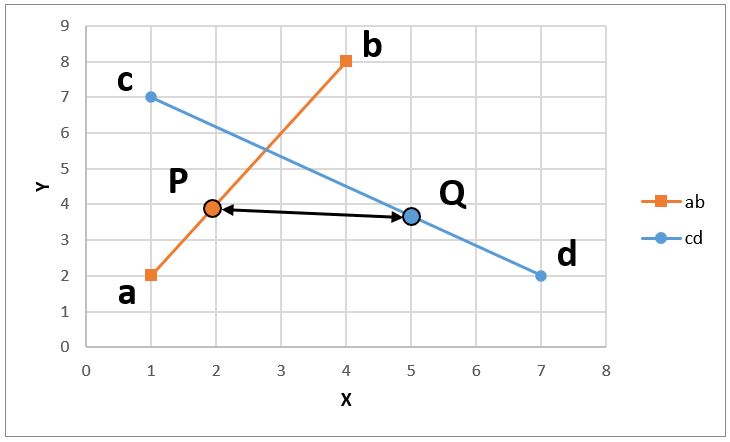
By calculating the distance towards various combinations, find the minimum distance point.
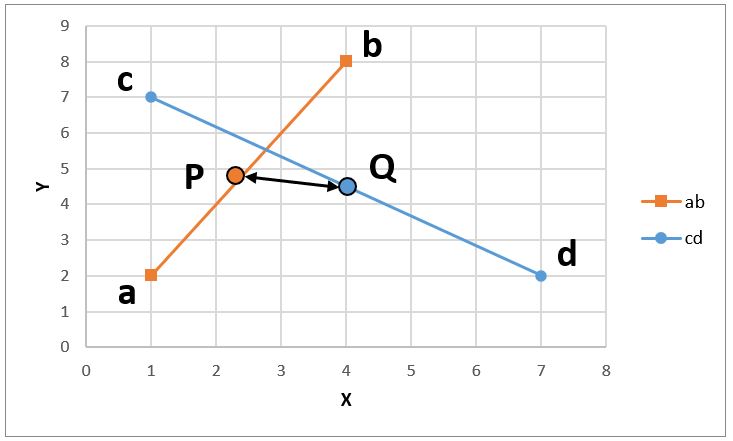
At the minimum distance points, coordinates of P & Q is coincide and it means the intersection coordinates.
I conduct this process by using python.
Introduction of Two Lines
Two lines is need for calculating above method, so at first, let’s designate the coordinates that consist two lines.
I designate the below coordinates.
a=[1,2]
b=[4,8]
c=[1,7]
d=[7,2]
It is like described on graph as shown below.
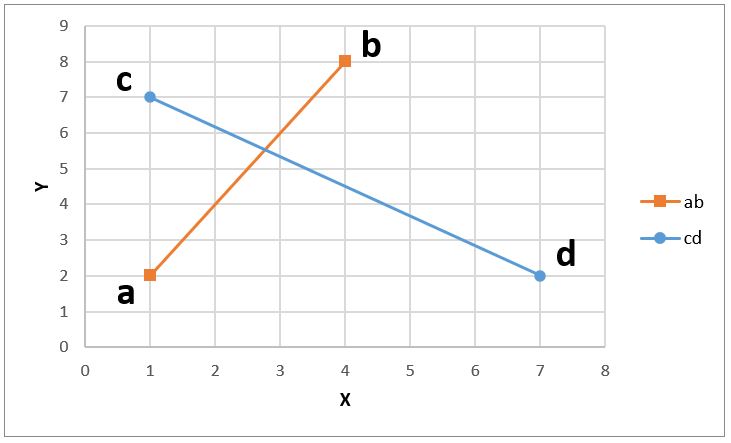
It is clear the intersection point exist on while X=2~3 and Y=5~6.
Sample Program of Calculating Intersection Coordinates
So much for the preface, let’s describe the program.
#import library
import numpy as np
#designate the coordinates of two lines.
a=[1,2]
b=[4,8]
c=[1,7]
d=[7,2]
#set the vector of two lines
line1=[a,b]
line2=[c,d]
a,b=line1[0],line1[1]
c,d=line2[0],line2[1]
ABbec=np.array([b[0]-a[0],b[1]-a[1]])
CDbec=np.array([d[0]-c[0],d[1]-c[1]])
#function of calculate two point distance
def calc_distance(s,t):
PQbec=(c+CDbec*s)-(a+ABbec*t)
distance=np.linalg.norm(PQbec)
return distance
#function of calculate point coordinates
def calc_pos(s,t):
Qpos=(c+CDbec*s)
Ppos=(a+ABbec*t)
return Ppos,Qpos
#function of searching minimun distance
def make_map(ss,tt):
z_list=[]
ij_list=[]
st_list=[]
for i in range(len(ss)):
for j in range(len(tt)):
s,t=ss[i],tt[j]
z=calc_distance(s,t)
z_list.append(z)
ij_list.append([i,j])
st_list.append([s,t])
return z_list,ij_list,st_list
#explore a large area
ini_max=2000
ini_min=-2000
delta=200
num_search=7
ss=np.linspace(ini_min,ini_max,delta)
tt=np.linspace(ini_min,ini_max,delta)
z,ij,st=make_map(ss,tt)
min_val=np.amin(np.array(z))
min_index=z.index(min_val)
#explore a neighborhood area of goal
minz_list=[]
for k in range(num_search):
i,j=ij[min_index][0],ij[min_index][1]
smax,smin=min(ss[i+2],ini_max),max(ss[i-2],ini_min)
tmax,tmin=min(tt[j+2],ini_max),max(tt[j-2],ini_min)
ss=np.linspace(smin,smax,delta)
tt=np.linspace(tmin,tmax,delta)
z,ij,st=make_map(ss,tt)
min_val=np.amin(np.array(z))
min_index=z.index(min_val)
minz_list.append(min_val)
Ppos,Qpos=calc_pos(st[min_index][0],st[min_index][1])
print('Ppos=')
print(Ppos)
print('Qpos=')
print(Qpos)
print('mean_pos=')
print((Qpos+Ppos)/2)
As I mentioned before, calculation is conducted exploratory in this method.
So, you should set the explore area first.
It is designated at “ini_max” and “ini_min” at middle of program.
And fineness and repeated number of exploration is designated at “delta” and “num_search”.
These four values should set appropriately.
Too large value can search correctly, but calculation time will longer.
Please adjust to suit your situation.
Result of Sample Program
Finally, let’s conduct the program shown above.
Below result wad shown.

This “mean_pos” is intersection coordinate.
Let’s compare the graph image.

The coordinate of program result is almost match above image.

I think this program is no problem.
That’s all. Thank you!!



コメント